Vage Egiazarian

I’m Research Scientist in deep learning. My research interests are model compression, LLM and generative networks. I have several papers at top Machine Learning conferences - NeurIPS, ICLR, SiGGRAPH, ICCV, ECCV e.t.c.
Papers
Extreme Compression of Large Language Models via Additive Quantization
Vage Egiazarian, Andrei Panferov, Denis Kuznedelev, Elias Frantar, Artem Babenko, Dan Alistarh
[Pre-print]
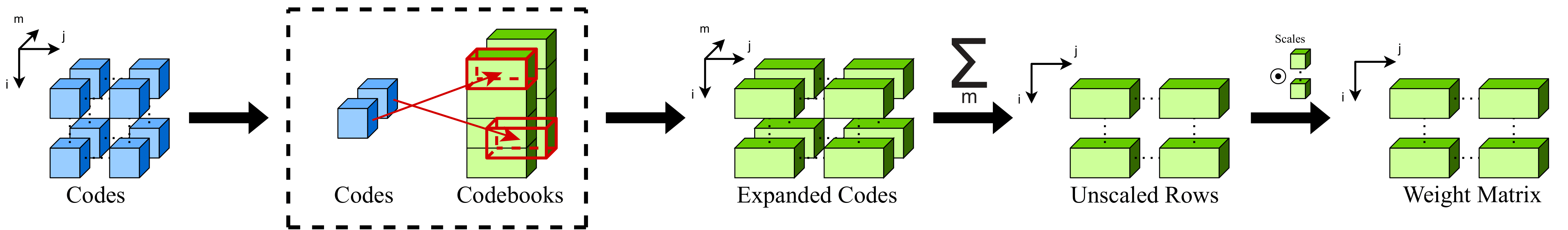
In this paper, we revisit the problem of “extreme” LLM compression–defined as targeting extremely low bit counts, such as 2 to 3 bits per parameter, from the point of view of classic methods in Multi-Codebook Quantization (MCQ). Our work builds on top of Additive Quantization, a classic algorithm from the MCQ family, and adapts it to the quantization of language models. The resulting algorithm advances the state-of-the-art in LLM compression, outperforming all recently-proposed techniques in terms of accuracy at a given compression budget.
SpQR: A Sparse-Quantized Representation for Near-Lossless LLM Weight Compression
Tim Dettmers, Ruslan Svirschevski, Vage Egiazarian, Denis Kuznedelev, Elias Frantar, Saleh Ashkboos, Alexander Borzunov, Torsten Hoefler, Dan Alistarh
[ICLR 2024]
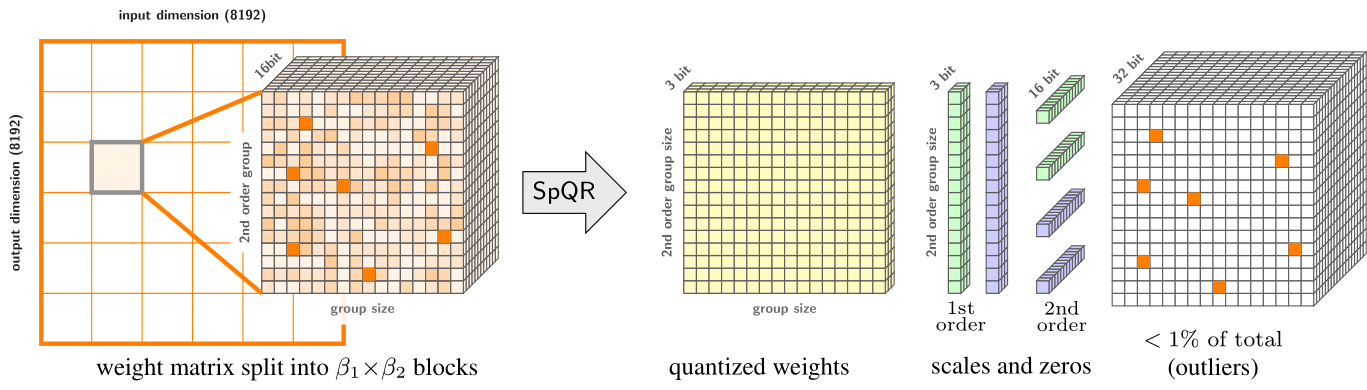
We introduce the Sparse-Quantized Representation (SpQR), a new compressed format and quantization technique which enables for the first time near-lossless compression of LLMs across model scales, while reaching similar compression levels to previous methods. SpQR works by identifying and isolating outlier weights, which cause particularly-large quantization errors, and storing them in higher precision, while compressing all other weights to 3-4 bits, and achieves relative accuracy losses of less than 1% in perplexity for highly-accurate LLaMA and Falcon LLMs.
Neural Optimal Transport with General Cost Functionals
Arip Asadulaev, Alexander Korotin, Vage Egiazarian,Petr Mokrov, Evgeny Burnaev
[ICLR 2024]
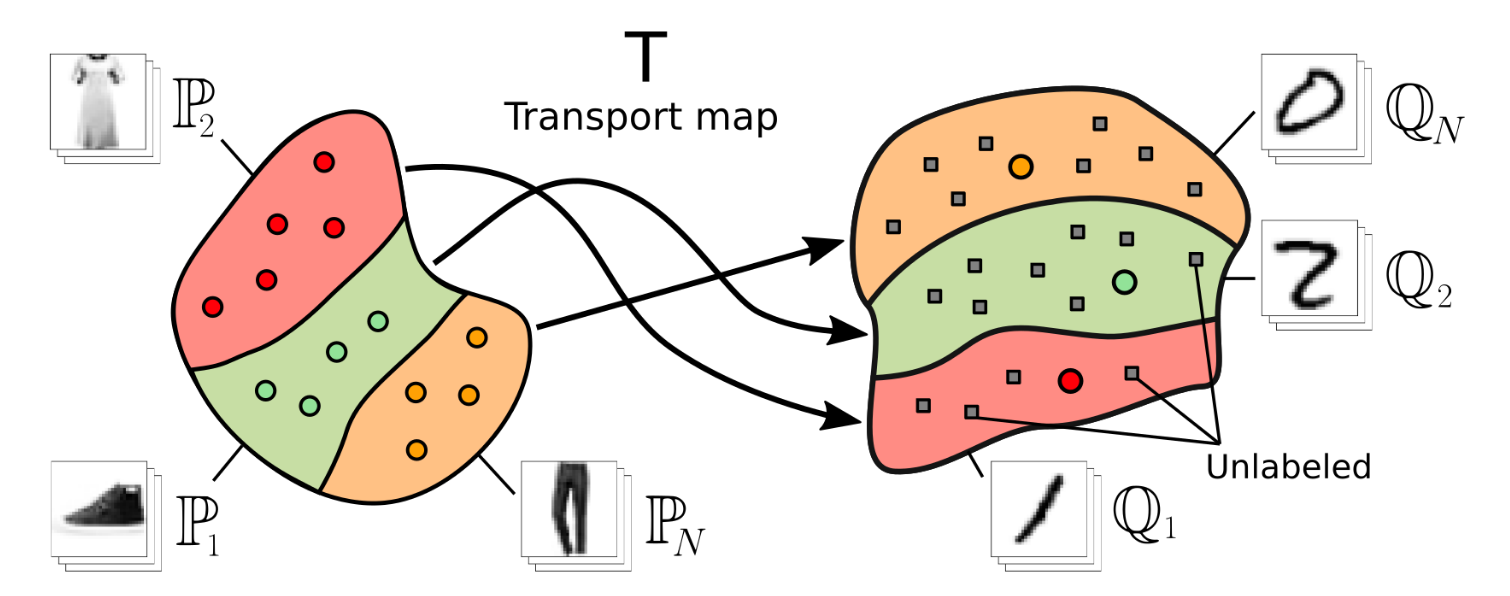
We present a novel neural-networks-based algorithm to compute optimal transport (OT) plans and maps for general cost functionals. The algorithm is based on a saddle point reformulation of the OT problem and generalizes prior OT methods for weak and strong cost functionals. As an application, we construct a functional to map data distributions with preserving the class-wise structure of data.
DEF: Deep Estimation of Sharp Geometric Features in 3D Shapes
Matveev,A., Rakhimov, R., Artemov, A., Bobrovskikh,G., Egiazarian,V., Bogomolov,E., Panozzo,D., Zorin,D., Burnaev,E.
[SiGGRAPH 2022]
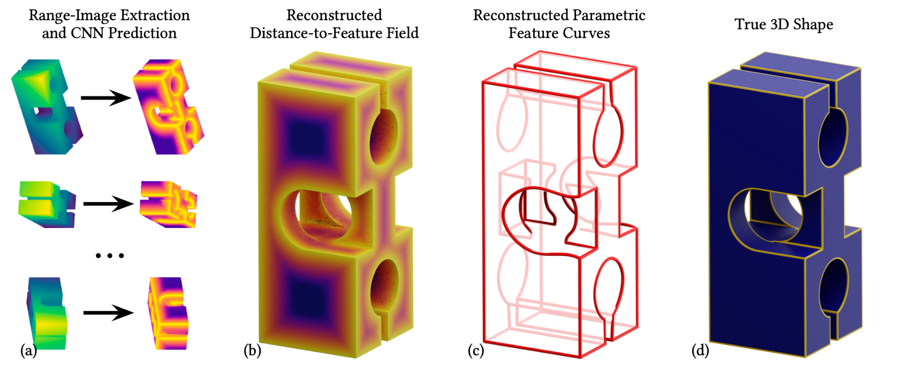
We propose Deep Estimators of Features (DEFs), a learning-based framework for predicting sharp geometric features in sampled 3D shapes. Differently from existing data-driven methods, which reduce this problem to feature classification, we propose to regress a scalar field representing the distance from point samples to the closest feature line on local patches. We demonstrate a downstream application, where we reconstruct an explicit representation of straight and curved sharp feature lines from range scan data.
Wasserstein Iterative Networks for Barycenter Estimation
Korotin, A., Egiazarian, V., Li, L., Burnaev E.
[NeurIPS 2022]
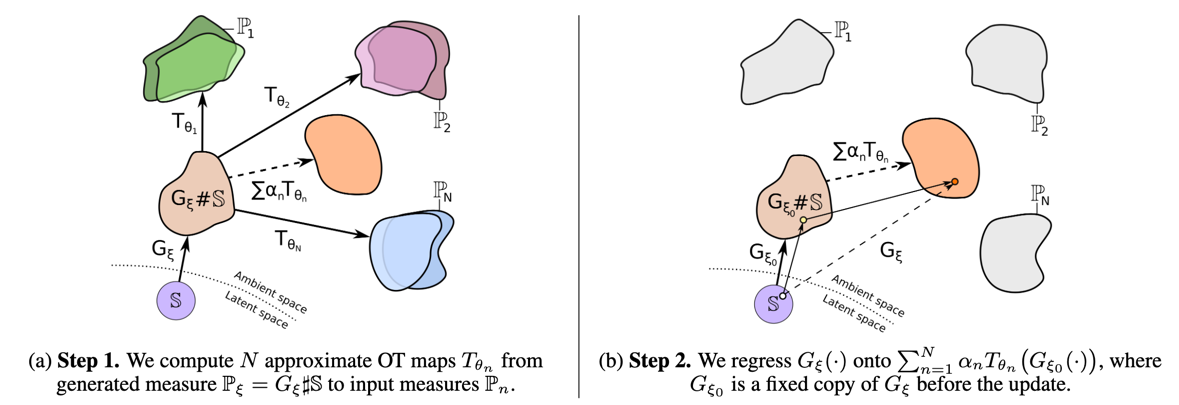
In this paper, we present an algorithm to approximate the Wasserstein-2 barycenters of continuous measures via a generative model. In addition, based on the celebrity faces dataset, we construct Ave, celeba! dataset which can be used for quantitative evaluation of barycenter algorithms.
Wasserstein-2 Generative Networks
Korotin, A., Egiazarian, V., Asadulaev, A., Burnaev E.
[ICLR 2021]
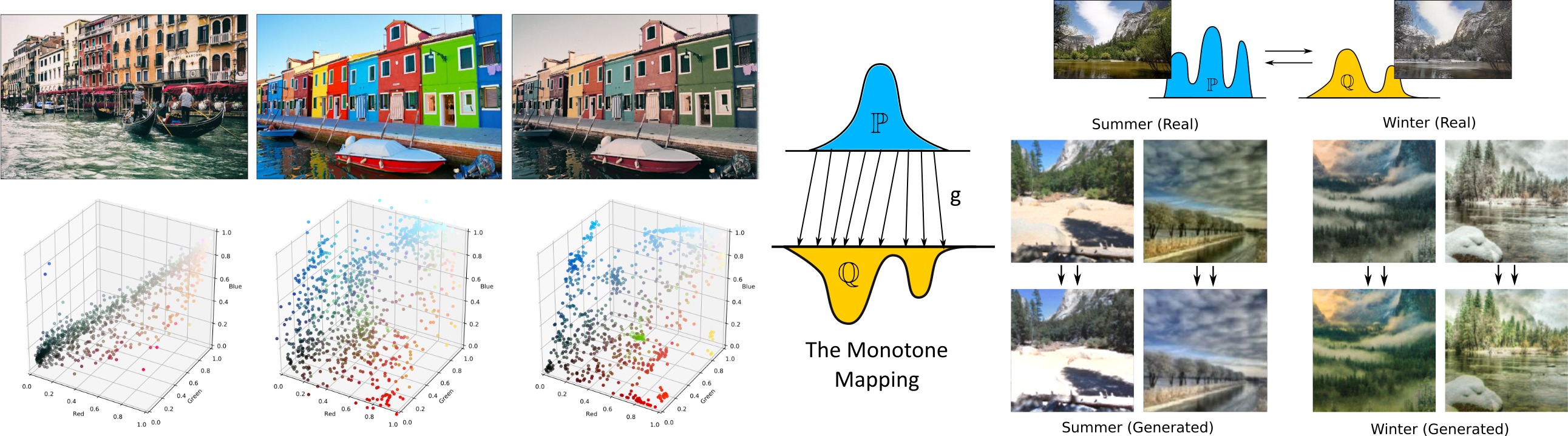
In this paper, we propose a novel end-to-end algorithm for training generative models which optimizes a non-minimax objective simplifying model training. The proposed algorithm uses the approximation of Wasserstein-2 distance by using Input Convex Neural Networks.
Deep Vectorization of Technical Drawings
Egiazarian,V.* , Voynov, O.* , Artemov, A., Volkhonskiy, D., Safin, A., Taktasheva, M., Zorin, D., & Burnaev, E.
[ECCV 2020]
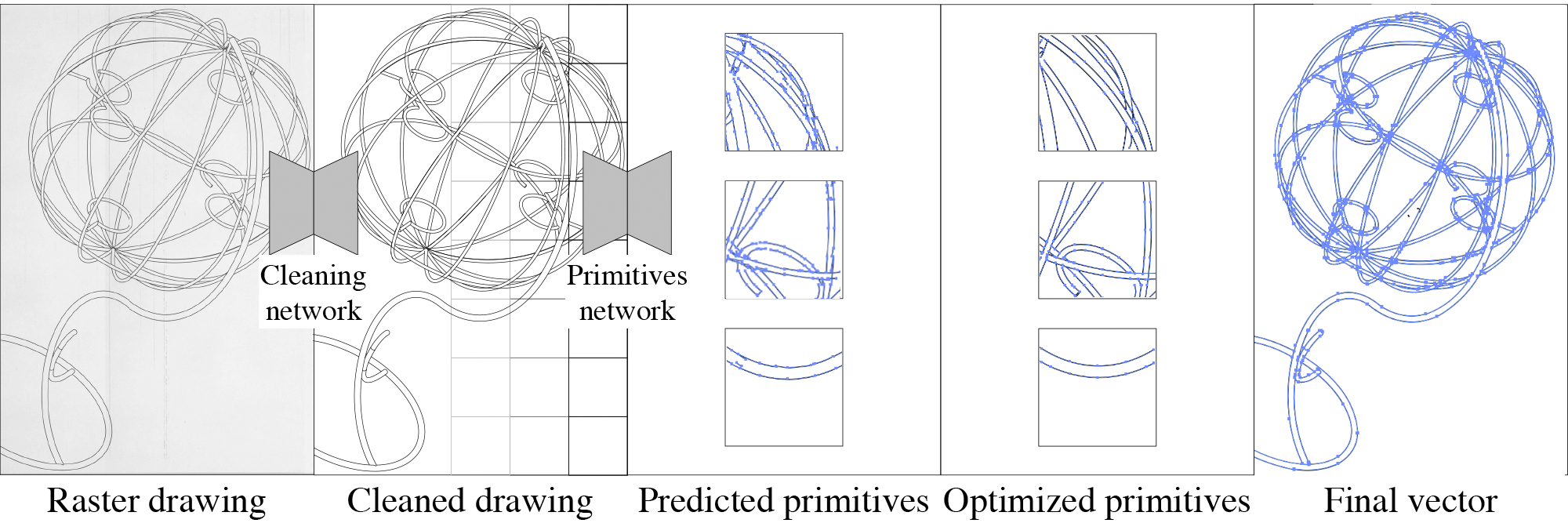
We present a new method for vectorization of technical line drawings which consists of (1) a deep learning-based cleaning stage, (2) a transformer-based network to estimate vector primitives, and (3) an optimization procedure to obtain the final primitive configurations.
Pyramids for Adversarial Representation Learning with 3D Point Clouds
Egiazarian, V.* , Ignatyev, S.* , Artemov, A., Voynov, O., Kravchenko, A., Zheng, Y., Velho,L., Burnaev,E.
[VISAPP 2020]
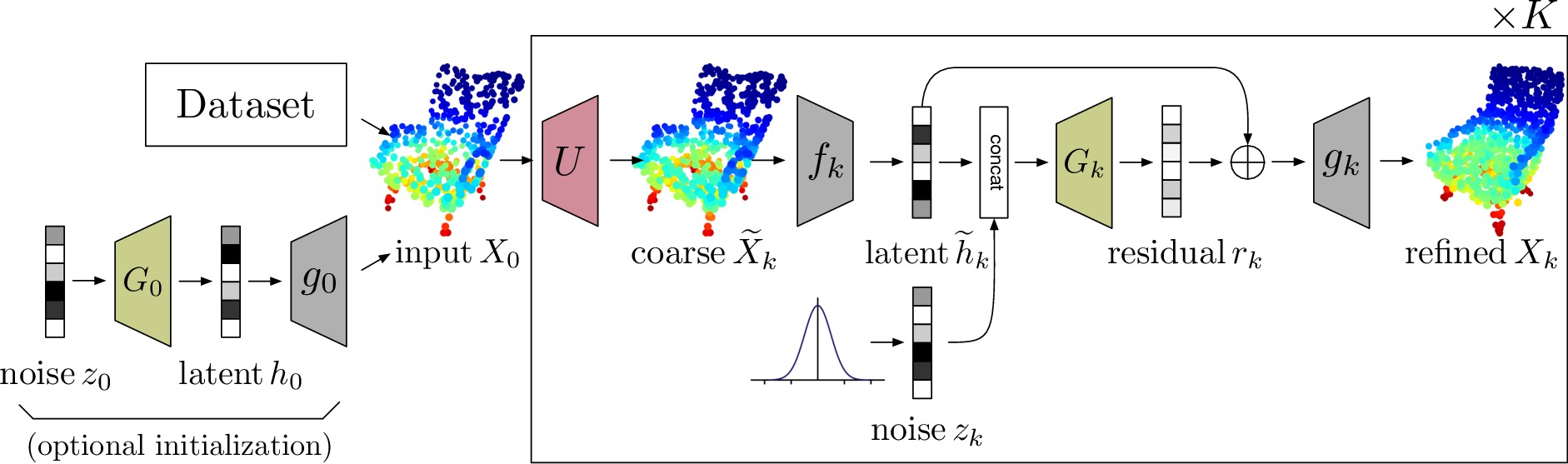
We employ a latent-space Laplacian pyramid representation within a hierarchical generative model for 3D point clouds. We combine recent latent-space GAN and Laplacian GAN to form a multi-scale model for generation of 3D point clouds with gradually increasing levels of detail.
Beyond Vector Spaces: Compact Data Representation as Differentiable Weighted Graphs
Denis Mazur, Vage Egiazarian, Stanislav Morozov*, Artem Babenko
[NeuRips 2019]
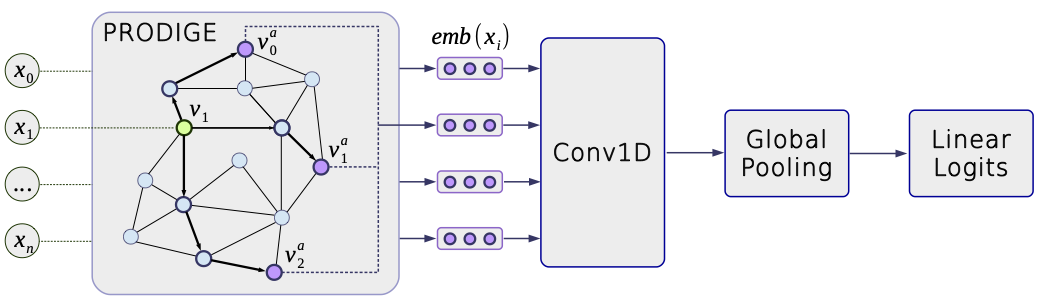
In this paper, we aim to eliminate the inductive bias imposed by the embedding space geometry. Namely, we propose to map data into more general non-vector metric spaces: a weighted graph with a shortest path distance. By design, such graphs can model arbitrary geometry with a proper configuration of edges and weights.
Perceptual deep depth super-resolution
Voinov, O., Artemov, A., Egiazarian, V., Notchenko, A., Bobrovskikh, G., Zorin, D., & Burnaev, E.
[ICCV 2019]
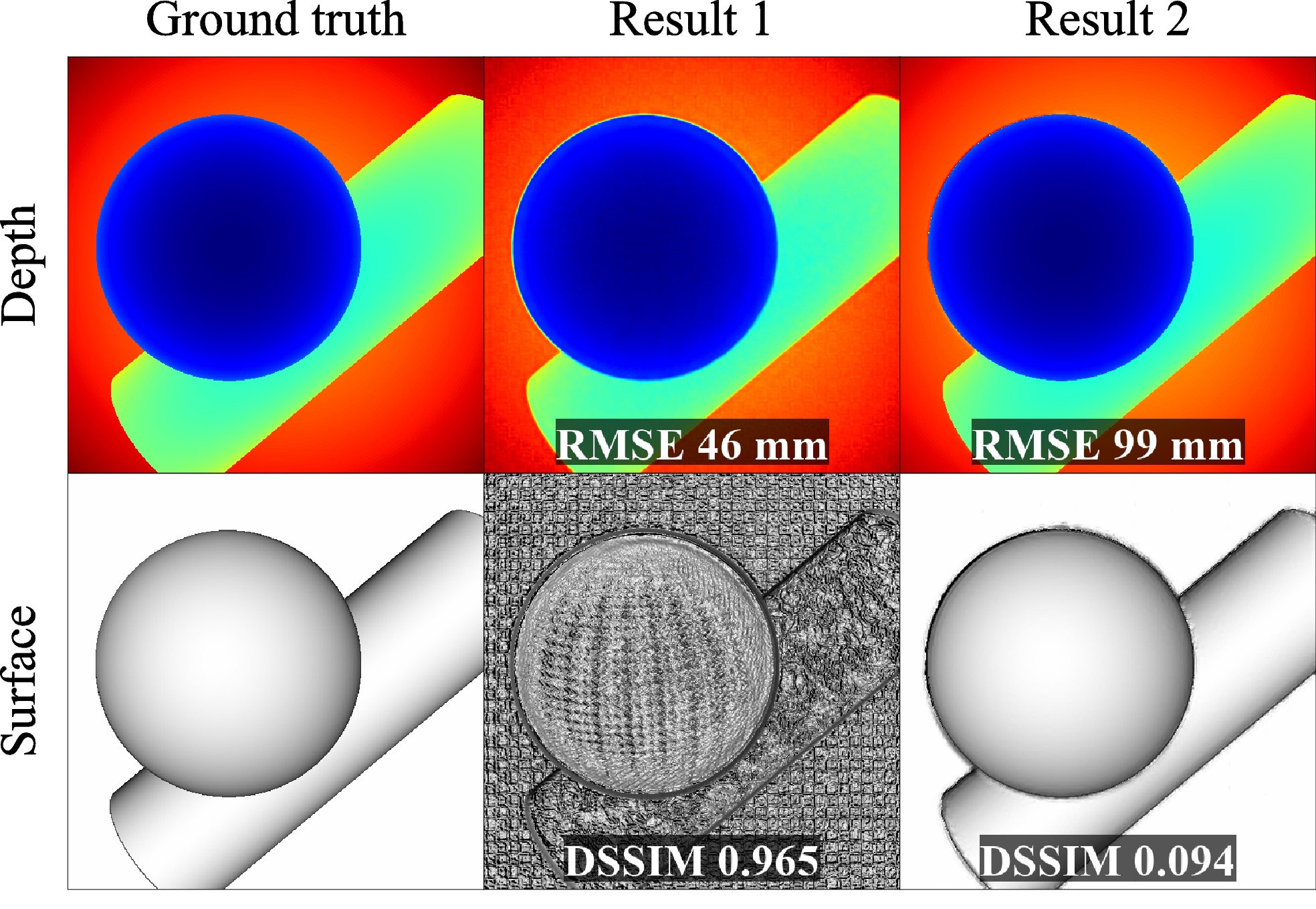
We address the problem of depth map super-resolution with the focus on visual quality of the corresponding 3D geometry. We demonstrate that basing the loss function on deviation of 3D surface rendering instead of direct depth deviation yields significantly improved results as measured by a number of perceptual metrics.
Awards
Laureate of Yandex The Ilya Segalovich Award 2020 for Researchers
Page template forked from evanca.>Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by orderedlist

